sequence to sequence¶
- seq2seq는 RNN과 출력하는 신경망을 조합한 모델
- 번역이나 챗봇 등 문장을 입력받아 다른 문장을 출력하는 프로그램에서 많이 사용
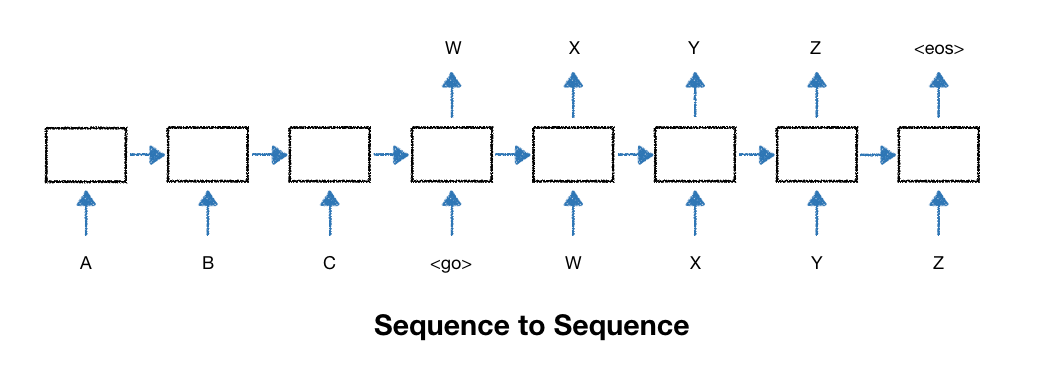
- seq2seq모델은 인코더와 디코더로 구성
- encoder는 원문을, decoder는 encoder의 결과물
- 후에 decoder가 출력한 결과물을 번역한 결과물과 비교하면서 학습

- symbol:
- decoder에 입력이 시작됨을 알려주는 symbol
- decoder의 출력이 끝났음을 알려주는 symbol
- 빈 데이터를 채울 때 사용하는 아무 의미가 없는 symbol
In [1]:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
char_arr = [c for c in "SEPabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz단어나무놀이소녀키스사랑봉구우루"]
num_dic = {n: i for i, n in enumerate(char_arr)}
dic_len = len(num_dic)
seq_data = [['word', "단어"], ["wood", "나무"], ["game", "놀이"], ["girl", "소녀"],
["kiss", "키스"], ["love", "사랑"], ["bong", "봉구"], ["uruu", "우루"]]
In [2]:
def make_batch(seq_data):
input_batch = []
output_batch = []
target_batch = []
for seq in seq_data:
input = [num_dic[n] for n in seq[0]]
output = [num_dic[n] for n in ("S" + seq[1])]
target = [num_dic[n] for n in (seq[1] + "E")]
input_batch.append(np.eye(dic_len)[input])
output_batch.append(np.eye(dic_len)[output])
target_batch.append(target)
return input_batch, output_batch, target_batch
In [3]:
learning_rate = 0.001
n_hidden = 128
total_epoch = 1000
n_class = n_input = dic_len
In [4]:
enc_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, None, n_input])
dec_input = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, None, n_input])
targets = tf.placeholder(tf.int64, [None, None])
In [5]:
# encoder: [batch size, time steps, input size]
# decoder: [batch size, time steps]
with tf.variable_scope("encode"):
enc_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicRNNCell(n_hidden)
enc_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(enc_cell, output_keep_prob=0.5)
outputs, enc_states = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(enc_cell, enc_input, dtype=tf.float32)
with tf.variable_scope("decode"):
dec_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicRNNCell(n_hidden)
dec_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(enc_cell, output_keep_prob=0.5)
outputs, dec_stats = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(dec_cell, dec_input,
initial_state=enc_states, dtype=tf.float32)
In [6]:
model = tf.layers.dense(outputs, n_class, activation=None)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
logits=model, labels=targets
)
)
opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)
In [7]:
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
input_batch, output_batch, target_batch = make_batch(seq_data)
cost_val = []
for epoch in range(total_epoch):
_, loss = sess.run([opt, cost], feed_dict={enc_input: input_batch,
dec_input: output_batch,
targets: target_batch})
cost_val.append(loss)
if (epoch+1) % 200 ==0:
print("Epoch: {:04d}, cost: {}".format(epoch+1, loss))
print("\noptimization complete")
In [9]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
plt.title("cost")
plt.plot(cost_val, linewidth=1, alpha=0.8)
plt.show()
- 입력으로 word를 받았다면 seq_data는 ["word", "PPPP"]로 구성될 것
- input_batch는 ["w", "o", "r", "d"], outout_batch는 ["P", "P", "P", "P"]글자들의 인덱스를 one-hot encoding한 값
target_batch는 각 글자의 인덱스인 [2, 2, 2 ,2]가 될 것
[batch_size, time step, input size]형태로 나오기 때문에 3번째 차원을 argmax로 취함
- 예측 결과는 글자의 인덱스를 뜻하는 숫자이므로 각 숫자에 해당하는 글자를 가져와 배열을 만듬
- 그리고 출력의 끝을 의미하는 "E"이후의 글자들을 제거하고 문자열로 만듬
- decoder의 입력(time steps) 크기만큼 출력값이 나오므로 최종 결과는 ["사", "랑", "E", "E"]처럼 나오기 때문
In [10]:
def translate(word):
seq_data = [word, "P" * len(word)]
input_batch, output_batch, target_batch = make_batch([seq_data])
prediction = tf.argmax(model, 2)
result = sess.run(prediction, feed_dict={enc_input: input_batch,
dec_input: output_batch,
targets: target_batch})
decoded = [char_arr[i] for i in result[0]]
try:
end = decoded.index("E")
translated = "".join(decoded[:end])
return translated
except Exception as ex:
pass
In [21]:
print("\n ==== translate test ====")
print("word -> {}".format(translate("word")))
print("wodr -> {}".format(translate("wodr")))
print("love -> {}".format(translate("love")))
print("loev -> {}".format(translate("loev")))
print("bogn -> {}".format(translate("bogn")))
print("uruu -> {}".format(translate("uruu")))
print("abcd -> {}".format(translate("abcd")))
In [12]:
from IPython.core.display import HTML, display
display(HTML("<style> .container{width:100% !important;}</style>"))
'Deep_Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 19.word2vec (0) | 2018.12.20 |
|---|---|
| 18.word2vec (0) | 2018.12.19 |
| 16.RNN_word_autoComplete (0) | 2018.12.18 |
| 15.RNN_mnist (1) | 2018.12.18 |
| 14.gan (0) | 2018.12.16 |
