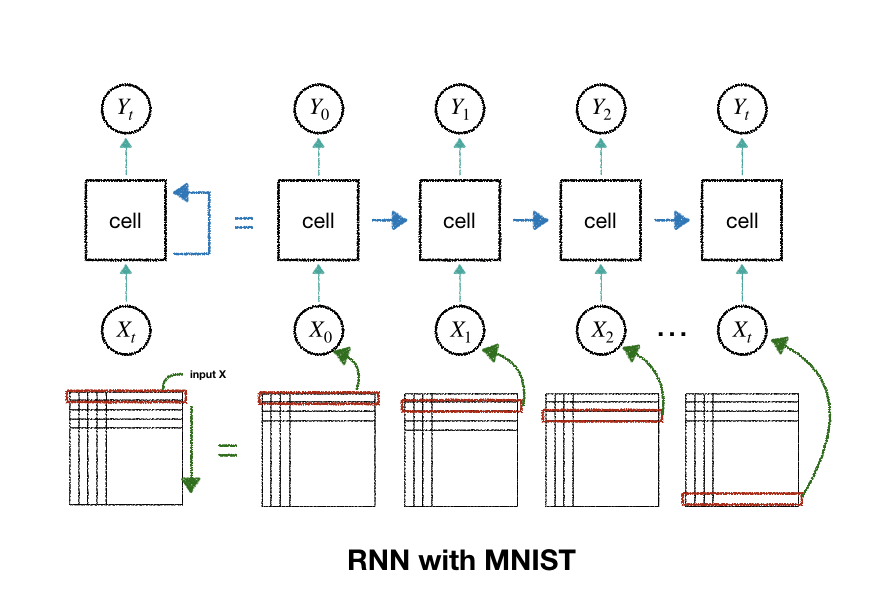
- 이 그림의 가운데에 있는 한 덩어리의 신경망을 RNN에서는 Cell이라 부름
- cell을 여러개 중첩하여 심층 신경망을 만듬
- 앞 단계에서 학습한 결과를 다음 단계의 학습에 이용
- 따라서 학습 데이터를 단계별로 구분하여 입력
- 사람은 글씨를 위에서 아래로 내려가면서 쓰는 경향이 많으므로
- 가로 한줄의 28 픽셀을 한 단계의 입력값으로 삼고
- 세로줄이 총 28개 이므로 28단계를 거쳐 데이터를 입력 받음
library load¶
In [1]:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
In [3]:
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("./mnist/data/", one_hot=True)
hyper parameter¶
- 입력값 X에 n_step이라는 차원을 하나 더 추가
- RNN은 순서가 있는 데이터를 다루므로 한 번에 입력 받을 갯수와 몇 단계로 이뤄진 데이터를 받을지를 설정
- 가로 픽셀 수를 n_input, 세로 픽셀 수를 입력 단계인 n_step으로 설정
- 앞에서 설명한 대로 RNN은 순서가 있는 데이터를 다루므로 한 번에 입력 받을 갯수와 총 몇 단계로 이뤄진 데이터를 받을지를 설정
- 가로 픽셀수: n_input, 세로 픽셀수: n_step
- 출력값은 계속해서 온 것처럼 MNIST의 분류인 0~9까지 10개의 숫자를 one-hot encoding으로 표현
In [4]:
learning_rate = 0.001
total_epoch = 30
batch_size = 128
n_input = 28
n_step = 28
n_hidden = 128
n_class = 10
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_step, n_input], name="input_X")
Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_class], name="output_Y")
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden, n_class], name="weight_W"))
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_class], name="bias_b"))
hidden개의 출력값을 갖는 RNN cell을 생성¶
In [5]:
cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicRNNCell(n_hidden)
- BasicLSTMCell, GRUCell 등 다양한 방식의 셀을 사용
- RNN의 기본신경망은 긴 단계의 데이터를 학습할 때 맨 뒤에서는 맨 앞의 정보를 잘 기억하지 못하는 특성이 존재
- 이를 보완하기 나온 것이 LSTMLong Short-Term Memory, GRUGated Recurrent Units
- GRU는 LSTM과 비슷하지만, 구조가 조금 더 간단한 신경망 Architecture
complete RNN¶
In [6]:
outputs, states = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, X, dtype=tf.float32)
- 결과값을 one-hot encoding 형태로 만들 것이므로 손실 함수로
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2를 사용 - 이 함수를 사용하려면 최종 결과값이
[batch_size, n_class]여야 함 - RNN 신경망에서 나오는 출력값은
[batch_size, n_step, n_hidden]
In [7]:
# outputs : [batch_size, n_step, n_hidden]
outputs = tf.transpose(outputs, [1, 0, 2]) # index를 기준으로 transpose
outputs = outputs[-1]
In [8]:
model = tf.matmul(outputs, W) + b
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits=model, labels=Y))
opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate).minimize(cost)
variable initializer¶
In [9]:
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(init)
In [10]:
x_train = mnist.train.images
y_train = mnist.train.labels
In [11]:
class Dataset:
def __init__(self, x, y):
self.index_in_epoch = 0
self.epoch_completed = 0
self.x_train = x
self.y_train = y
self.num_examples = x.shape[0]
def data(self):
return self.x_train, self.y_train
def next_batch(self, batch_size):
start = self.index_in_epoch
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.index_in_epoch += self.batch_size
if start==0 and self.epoch_completed==0:
idx = np.arange(self.num_examples)
np.random.shuffle(idx)
self.x_train = self.x_train[idx]
self.y_train = self.y_train[idx]
if start + batch_size > self.num_examples:
self.epoch_completed += 1
perm = np.arange(self.num_examples)
np.random.shuffle(perm)
self.x_train = self.x_train[perm]
self.y_train = self.y_train[perm]
start = 0
self.index_in_epoch = self.batch_size
end = self.index_in_epoch
return self.x_train[start:end], self.y_train[start:end]
In [12]:
total_batch = int(x_train.shape[0]/batch_size)
epoch_cost_val_list = []
cost_val_list = []
for epoch in range(total_epoch):
epoch_cost = 0
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs, batch_ys = Dataset(x=x_train, y=y_train).next_batch(batch_size=batch_size)
batch_xs = batch_xs.reshape([batch_size, n_step, n_input])
_, cost_val = sess.run([opt, cost], feed_dict={
X: batch_xs, Y: batch_ys
})
epoch_cost += cost_val
cost_val_list.append(cost_val)
epoch_cost_val_list.append(epoch_cost)
if (epoch+1) %5 == 0:
print("Epoch: %04d" % (epoch+1),
"Avg.cost = {}".format(epoch_cost/total_batch))
print("\noptimization complete")
is_correct = tf.equal(tf.argmax(model, 1), tf.argmax(Y, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(is_correct, tf.float32))
test_batch_size = len(mnist.test.images)
test_xs = mnist.test.images.reshape(test_batch_size, n_step, n_input)
test_ys = mnist.test.labels
print("\naccuracy {:.3f}%".format(
sess.run(accuracy*100, feed_dict={X: test_xs, Y: test_ys})
))
In [14]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False
_, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(20, 5))
ax[0].set_title("cost_epoch")
ax[0].plot(epoch_cost_val_list, linewidth=0.3)
ax[1].set_title("cost_value")
ax[1].plot(cost_val_list, linewidth=0.3)
plt.show()
In [16]:
from IPython.core.display import HTML, display
display(HTML("<style> .container{width:100% !important;}</style>"))
'Deep_Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 17.seq2seq (0) | 2018.12.19 |
|---|---|
| 16.RNN_word_autoComplete (0) | 2018.12.18 |
| 14.gan (0) | 2018.12.16 |
| 13.auto-encoder (0) | 2018.12.15 |
| 12.mnist_cnn (0) | 2018.12.12 |
